
Retaining Wall Lecture 6 Counterfort Retaining Wall Design YouTube
🕑 Reading time: 1 minuteCantilever retaining wall are usually of reinforced concrete and work on the principles of leverage. It has much thinner stem and utilize the weight of the backfill soil to provide most of the resistance to sliding and overturning. Cantilever retaining wall is the most common type of earth-retaining structure. It is […]
amudu RETAINING WALL
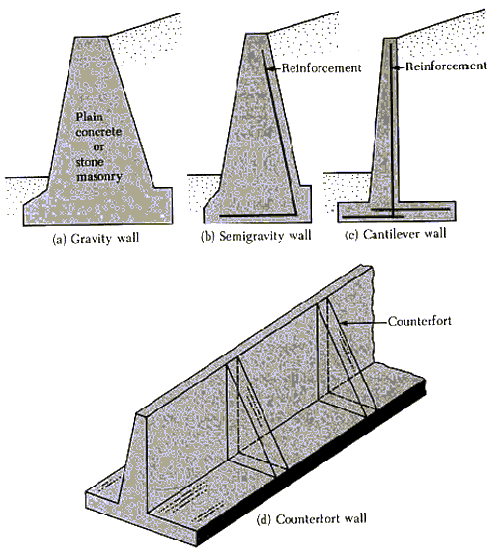
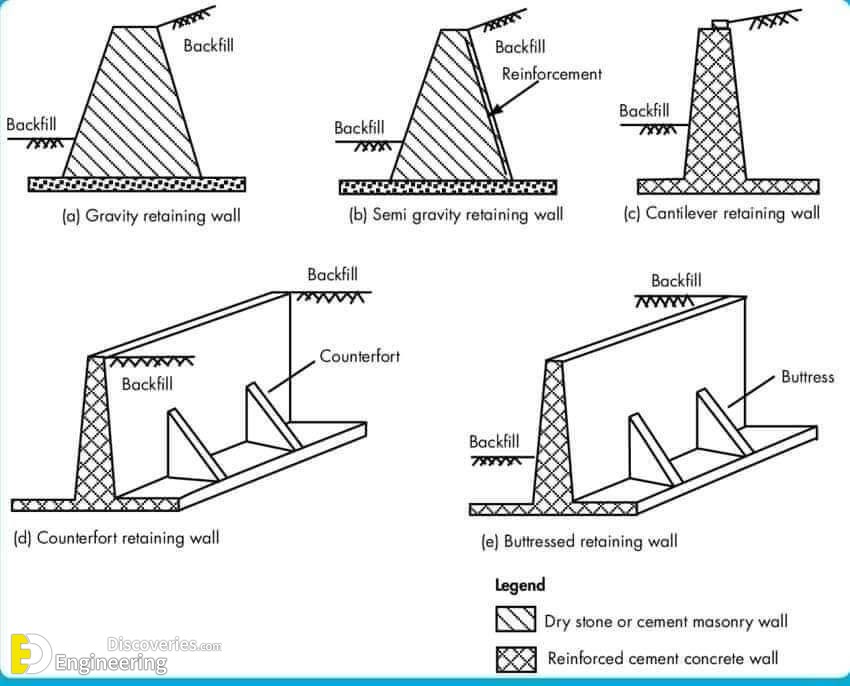
Cantilever does not required any support. Counter fort are provided as support. Economical below 6-7 m height. Economical above 7 m high. Uniformity of stress is not maintained. Uniformity of stress is maintained. All components are considered as slab. Counter fort itself is considered as beam, rest all components are considered slab.

the diagram shows how to install a concrete retaining wall with drainage and grounding options
A counterfort-relief shelf composite retaining wall is capable of reducing lateral earth pressure. With its relief shelf and T-shape variable section beam as tension member, this wall is effective for high fill slope engineering; however, research on this type of retaining wall is limited. Moreover, investigating the lateral earth pressure distribution law and the mechanical and deformation.
Retaining wall Types and Applications Learn Everything Civil and structural engineering
Walls Counterfort Retaining Wall Definitions & Advantages | Counterfort Retaining Wall Design Example Counterfort Retaining Wall | How is Counterfort Retaining Wall Done? | Advantages of Counterfort Retaining Wall | Counterfort Retaining Wall Vs Cantilever Retaining Walls What Is a Counterfort Retaining Wall?

7 Different Types of Retaining Walls Which One is the Right Fit for You? Organize With Sandy
Contents show What Is Retaining Wall? It is a structure constructed to retain materials such as soil and maintain the surface of the ground at different elevations on either side of it. In this article, we've discussed different types of retaining walls.

Cantilever Retaining Wall Counterfort Retaining Wall Retaining Wall
1. Introduction Cantilever retaining wall is widely used for cross-drainage works, for maintaining slope stability, for road embankments, etc. Sometimes retaining walls cause serious damage due to earthquakes and other dynamic forces.

9 Types of Retaining wall and their properties (What is a retaining wall?) civilogy YouTube
For diaphragm cantilever walls it is unlikely that friction between the soil and the wall will be developed because the wall is expected to settle along with the earth fill (small bearing capacity). Therefore, it is preferable to assume δ=0 and use Rankine's theory. For anchored diaphragm walls, the values illustrated in Table 1 can be used.

Retaining Walls Explained Types, Forces, Failure and Reinforcement Structures Explained
Counterfort retaining walls are more economical than cantilever walls for heights above 25 ft. Gravity Poured Concrete Retaining Walls Gravity retaining walls depend on their own weight and any soil resting on the concrete in resisting lateral earth forces. They are generally economical up to 10 feet in height for cast concrete structures.
RCC Retaining Wall (Cantilever Type) Excel Sheet Engineering Discoveries
Cantilever retaining walls are found best up to a height of 6m.For greater heights earth pressure due to retained fill will be higher due to lever arm effect, higher moments are produced at base, which leads to higher section for stability design as well as structural design. This proves to be an uneconomical design.

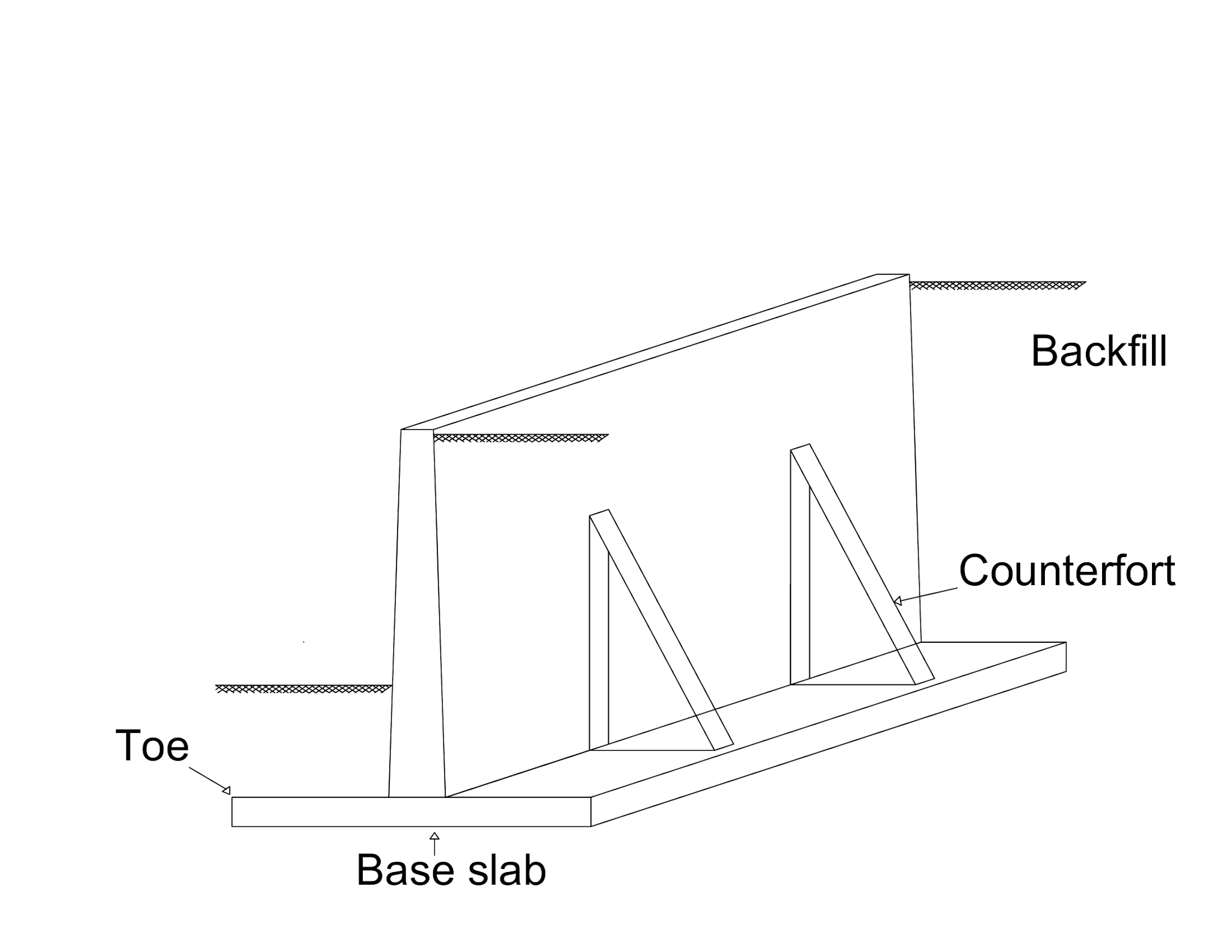
Counterfort Retaining Wall Its 4 Parts & Advantages
A counterfort is basically a cantilever beam that serves the purpose of tying the wall's stem and the wall base together. This way the internal stress distribution in the wall is greatly reduced while the stability of the wall is also enhanced. This focus of this article is on designing a counterfort retaining wall.

Retaining Walls Explained Types, Forces, Failure and Reinforcement Structures Explained
Cantilever retaining wall vs. counterfort retaining wall Cantilever retaining wall vs. counterfort retaining wall ars001 (Structural) (OP) 21 Aug 07 11:53.. I have designed cantilever, buttress & counterfort walls up to 10 m depth. Checking several designs (some years ago), the optimum maximum height for a cantilever wall was about 6 m.
Design Of Retaining Wall With Counterfort Engineering Discoveries
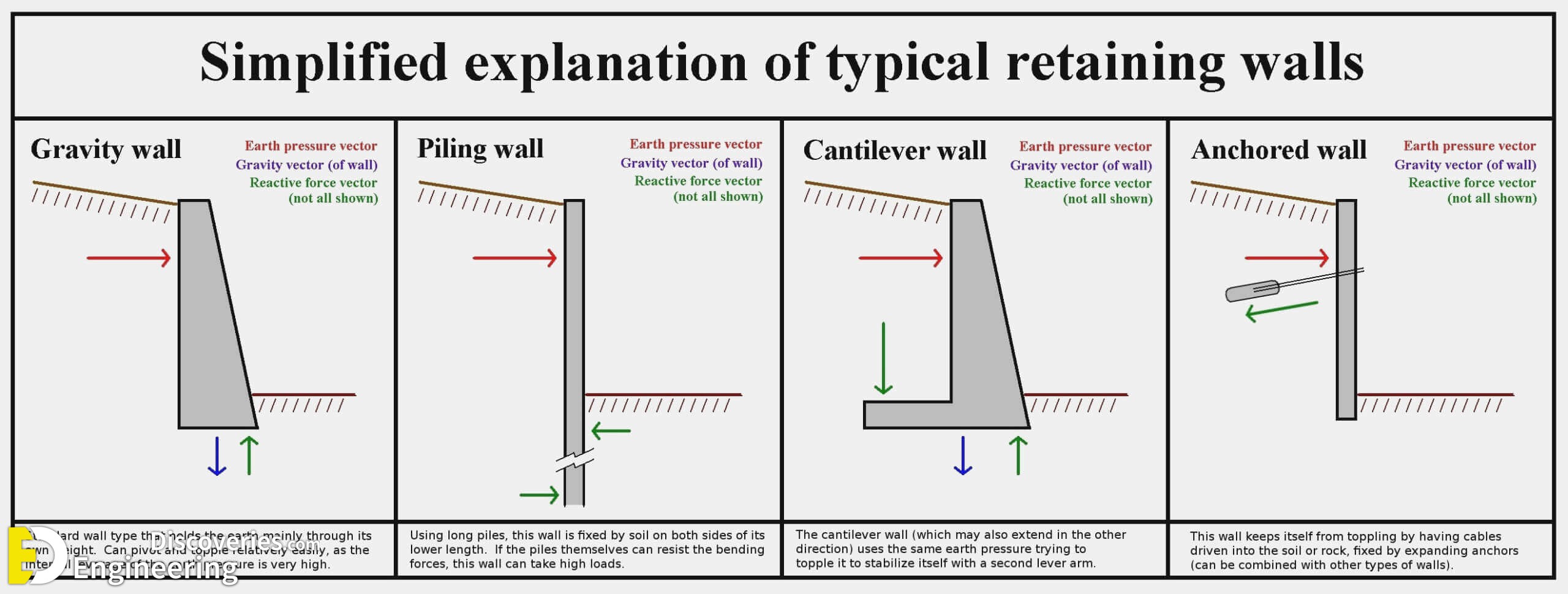
Cantilever concrete retaining walls have the same thickness from top to bottom and a very wide support footing. Buttressed walls are similar to the counterfort type but face in the opposite direction. Anchored retaining walls are mechanically supported by tethers. Gravity concrete retaining walls are the most commonly used type and typically.

19 Types of Retaining Wall Materials and Designs for Your Yard (2023)
Walls, used to retain masses of earth or other loose material in a vertical (or nearly vertical) position at locations where an abrupt change in ground level occurs, are called as 'retaining walls'.

How to build retaining wall Counterfort retaining wall reinforcements step by step 3d
A retaining wall is a rigid structure build to retain the soil or the masses of debris at one end having different levels so that the soil masses don't slip from it. Thus, retaining walls are specially designed for lateral earth pressure and forces.

Design of cantilever and counter fort retaining walls Retaining wall Retains Earth when
In cantilever retaining wall the pressure and other forces are withstand by the stem of the retaining wall and base slab. In counterfort retaining wall is provided the height of retaining wall is more than 6m. the walls also provided perpendicular to stem wall. The counterfort act as support to stem and heel slab.

Types of retaining walls
Cantilever Retaining Wall Vs Counterfort Retaining Wall: What is a Cantilever Retaining Wall? These are short structures consisting of a thin wall referred to as the stem, which is usually connected to a horizontal slab or plate called its footing. The wall goes deeper into the soil, where it rests on a more robust base material.